Bringing your natural smile to life...
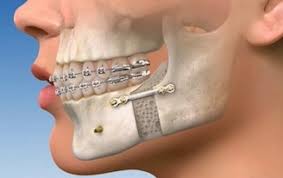
Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery is an operation to reposition the upper, lower, or both jaws.
People with jaw size/position discrepancies are usually affected with a malocclusion (poorly aligned teeth and bite) which is usually treated using orthodontics (braces) alone. However with severe jaw discrepancies orthognathic surgery is required and patients can be adversely affected in many ways:
- Psychological distress which will affect interpersonal relationships and quality of life due to a severely compromised dental and facial appearance.
- Jaw muscle and jaw joint problems.
- Speech difficulties.
- Jaw function is compromised which can result in difficulty eating certain foods.
- Damage caused to the gums and palate arising from a traumatic bite may compromise the prognosis of the teeth into the future.
A jaw discrepancy is usually hereditary but can develop without a specific cause. Occasionally jaw discrepancies arise as a result of a growth disturbance, for example: following a jaw fracture in childhood or repair of a cleft lip or palate. A jaw discrepancy may be detected in early childhood but becomes more marked during puberty. The unusual jaw growth usually ceases in late adolescence and treatment is directed towards correction of the deformity once growth is complete.